Educational Research in Chemistry
1. Green Chemistry CURE
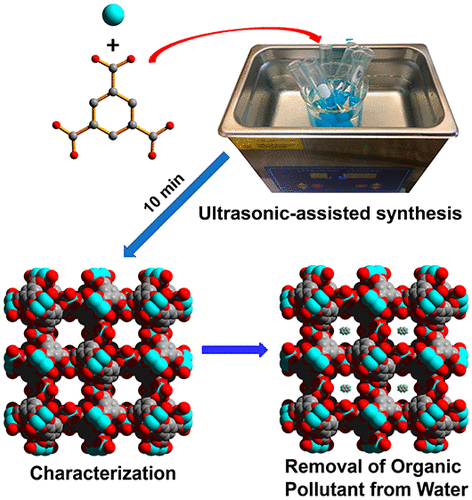
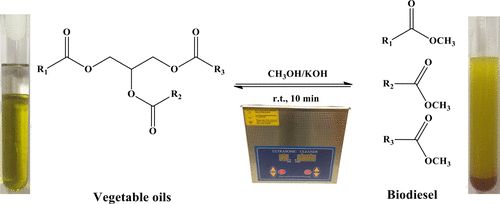
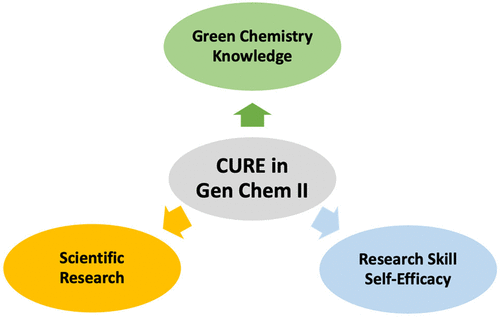
In response to growing environmental challenges and shifting educational priorities, integrating green chemistry into undergraduate teaching labs offers a powerful strategy to advance both learning and sustainability. Our group is interested in developing new Green Chemistry CURE projects for STEM majors or non-STEM majors and implementing the CURE projects in different undergraduate chemistry laboratory courses.
2. Investigating student affects in different learning environments
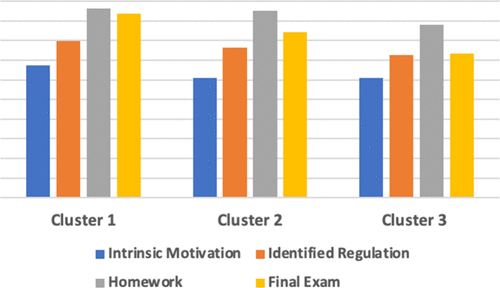
Student affect includes attitudes, motivation, values, beliefs, self-efficacy, opinions, emotions, interests, etc. Affect is one of the most important factors influencing students’ thinking and behaviors in social contexts like in classrooms. The affective constructs play an important role in developing meaningful understanding of scientific concepts, including chemistry concepts. Therefore, as a way to understand the role of different affective variables on students’ achievement and retention in STEM, our group is interested in exploring the overall status of student affects using theory-based instruments, the impact of learning environments, and whether there are any differences among different underrepresented groups. The results will help us design and implement interventions to improve student learning and retention.